
We are so excited to bring you the first public beta of the next generation of ColdBox HMVC , version 6.0. This version has been in development for quite some time now and it is introducing some revolutionary new programming techniques for ColdFusion (CFML) developers. This major bump is a huge leap into modern programming and breaksthrough to the next generation of apps we are building at Ortus. Enjoy!
Installation
You can easily install this beta version by using the following CommandBox install string:
1 |
install coldbox@6.0.0-beta-snapshot |
You can also continue to use the bleeding edge as we incorporate fixes and the latest updates to the core:
1 |
install coldbox@be |
Bug Reporting & Collaboration
If you do find any bugs with this beta or just want to collaborate with more ideas for this release, please make sure you head out to our Jira instance at: https://ortussolutions.atlassian.net/secure/RapidBoard.jspa?rapidView=22&projectKey=COLDBOX.
You can also contact us at the following Slack locations:
- CFML Slack
box-productschannel - Box Team Slack : boxteam.herokuapp.com
What's New With 6.0.0
ColdBox 6.0.0 is a major release for the ColdBox HMVC platform. It has some dramatic new features as we keep pushing for more modern and sustainable approaches to web development. We break down the major areas of development below and you can also find the full release notes per library at the end.
Engine Support
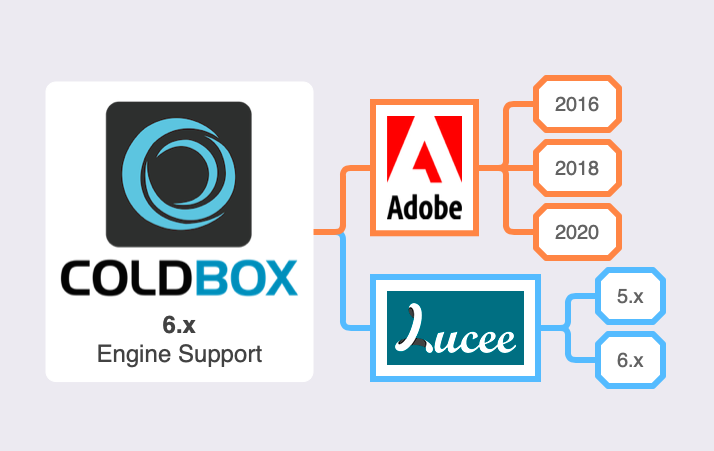
It is also yet another source code reduction due to the dropping of support for the following CFML Engines:
- Adobe ColdFusion 11
- Luce 4.5
The info-graphic above shows you the supporte engines the 6.x platform will support.
Asynchronous Programming
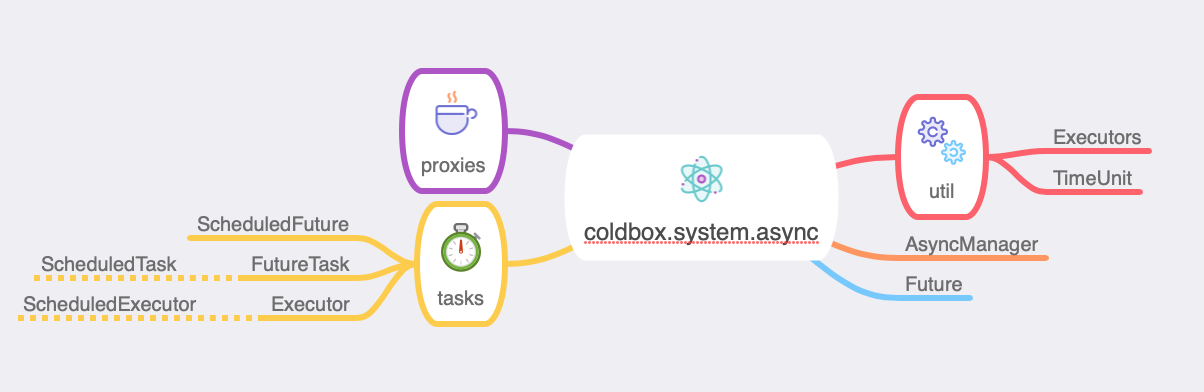
We have done a tremendous amount of work to expose all the async and parallel programming constructs in ColdBox to the entire framework so developers can leverage them. There is just so much we have done on this release for concurrency, task scheduling, and parallel programming to include in one page. So visit our Async Programming section to start delving into what we are lovingly calling cbFutures!
ColdBox Executors & Tasks
Thanks to our new futures approach, all major internal libraries (WireBox, CacheBox, LogBox, MVC) will leverage them for different tasks that require asynchronicity and scheduling. You will see a noticeble difference especially in the following areas:
- Cache Reaping: All cache reaping is now done via a scheduled task running on specific frequencies
- File Appenders: It uses an async schedule to stream log data to files instead of blocking operations for sending logs. It will use a logging in-memory queue to stream the log data to the file. So you can potentially send 10000 log events and eventually they will be streamed to disk.
What are ColdBox Futures?
A ColdBox future is used for async/parallel programming where you can register a task or multiple tasks that will execute in a non-blocking approach and trigger dependent computations which could also be asynchronous. This Future object can then be used to monitor the execution of the task and create rich completion/combining pipelines upon the results of such tasks. You can still use a get() blocking operation, but that is an over simplistic approach to async programming because you are ultimately blocking to get the result.
ColdBox futures are backed by Java's CompletableFuture API, so the majority of things will apply as well; even Java developers will feel at home. It will allow you to create rich pipelines for creating multiple Futures, chaining, composing and combining results.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
// Parallel Executionsasync().all( () => hyper.post( "/somewhere" ), () => hyper.post( "/somewhereElse" ), () => hyper.post( "/another" )).then( (results)=> logResults( results ) );// Race Conditions, let the fastest dns resolvevar dnsServer = async().any( () => dns1.resolve(), () => dns2.resolve()).get();// Process an incoming orderasync().newFuture( () => orderService.getOrder() ) .then( (order) => enrichOrder( order ) ) .then( (order) => performPayment( order ) ) .thenAsync( (order) => dispatchOrder( order ), async().getExecutor( "cpuIntensive" ) ) .then( (order) => sendConfirmation( order ) );// Combine Futuresvar bmi = async().newFuture( () => weightService.getWeight( rc.person ) ) .thenCombine( async().newFuture( () => heightService.getHeight( rc.person ) ), ( weight, height ) => { var heightInMeters = arguments.height/100; return arguments.weight / (heightInMeters * heightInMeters ); } ) .get();// Compose Futures with exceptionsasync() .newFuture( () => userService.getOrFail( rc.id ) ) .thenCompose( ( user ) => creditService.getCreditRating( user ) ) .then( (creditRating) => event.getResponse().setData( creditRating ) ) .onException( (ex) => event.getResponse().setError( true ).setMessages( ex.toString() ) ); |
See https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/CompletableFuture.html
This new approach to creating async pipelines and parallel processing, will further create extensibility and robustness in your ColdBox applications.
RestHandler & ColdBox Response
After many years of adding a base handler and a response object to our application templates, we finally have integrated them into the core so developers can have even more support when building RESTFul services. This new rest handler will provide you with tons of utilities and approaches to make all of your RESTFul services:
- Uniform
- Consistent
- A consistent and extensible response object
- Error handling
- Invalid Route handling
- Much more
Base Class
New base class coldbox.system.RestHandler which you can inherit from or use our new restHandler annotation. This will give you access to our enhanced API utilities and the native response object via the request context's getResponse() method.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
component extends="coldbox.system.RestHandler"{ function index( event, rc, prc ){ event.getResponse() .setData( "Hello from restful Land" ); }}component resthandler{ function index( event, rc, prc ){ event.getResponse() .setData( "Hello from restful Land" ); } } |
You can now build all of your api’s using the native response object like the rest templates, but now from the core directly. This Rest Handler gives you the following actions out of the box:
| Core Actions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| aroundHandler() | Wraps all rest actions uniformly to provide consistency and error trapping. |
| onError() | An implicit error handler is provided just in case anything explodes in your restful actions. Sends an appropriate 500 error |
| onValidationException() | Traps any {{ValidationException }}and makes sure it sends the appropriate 400 response with the invalid data. Useful for using cbValidation |
| onEntityNotFoundException() | Traps any {{EntityNotFound }}or {{RecordNotFound }}exceptions and makes sure it send an appropriate 404 response. Useful for leveraging cborm or Quick ORM |
| onInvalidHTTPMethod() | Traps any invalid HTTP method security exception and sends the appropriate 405 not allowed response |
| onMissingAction() | Traps any invalid actions/resource called in your application and sends the appropriate 404 response |
| onAuthenticationFailure() | Traps InvalidCredentials exceptions and sends the appropriate 403 invalid credentials response. If you are using cbSecurity it will also verify jwt token expiration and change the error messages accordingly. |
| onAuthorizationFailure() | Action that can be used when a user does not have authorization or access to your application or code. Usually you will call this manually or from a security library like cbSecurity or cbGuard. It will send a 401 not authorized response. |
| onInvalidRoute() | Action that can be used as a catch all from your router so it can catch all routes that are invalid. It will send a 404 response accordingly. |
| onExpectationFailed() | Utility method for when an expectation of the request fails ( e.g. an expected parameter is not provided ). This action is called manually from your own handlers and it will output a 417 response back to the user. |
AroundHandler in Detail
The aroundHandler() provided in the RestHandler will intercept all rest calls in order to provide consistency and uniformity to all your actions. It will try/catch for major known exceptions, time your requests, add extra output on development and much more. Here are a list of the features available to you:
- Exception Handling
- Automatic trapping of the following exceptions:
InvalidCredentials, ValidationException, EntityNotFound, RecordNotFound - Automatic trapping of other exceptions
- Logging automatically the exception with extra restful metadata
- If in a
developmentenvironment it will respond with much more information necessary for debugging both in the response object and headers
- Automatic trapping of the following exceptions:
- Development Responses
- If you are in a
developmentenvironment it will set the following headers for you:x-current-routex-current-routed-urlx-current-routed-namespacex-current-event
- If you are in a
- Global Headers
- The following headers are sent in each request
x-response-time: The time the request took in CFx-cached-response: If the request is cached via event caching
- The following headers are sent in each request
The aroundHandler() is also smart in detecting the following outputs from a handler:
- Handler
returnresults - Setting a view or layout to render
- Explicit
renderData()calls
RequestContext Additions
getResponse()- Will get you the current
prc.responseobject, if the object doesn’t exist, it will create it and set it for you - The core response object can be found here:
coldbox.system.web.context.Response
- Will get you the current
Extending The RestHandler
If you would like to extend or modify the behavior of the core RestHandler then you will have to create your own base handler that inherits from it. Then all of your concrete handlers will inherit from your very own handler.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
// BaseHandlercomponent extends="coldbox.system.Resthandler"{ // Modify it here}// Then make your own handlers extend from itcomponent extends="BaseHandler"{} |
Extending The Response Object
The response object can be found here: coldbox.system.web.context.Response and the rest handler constructs it by calling the request context’s getResponse() method. The method verifies if there is a prc.response object and if it exists it returns it, else it creates a new one. So if you would like to use your very own, then just make sure that before the request you place your own response object in the prc scope.
Here is a simple example using a preProcess() interceptor in your config/Coldbox.cfc:
1 2 3 |
function preProcess( event, interceptData, rc, prc ){ prc.response = wirebox.getInstance( "MyResponseObject" );} |
That’s it. Once that response object is in the prc scope, ColdBox will utilize it. Just make sure that your custom Response object satisfies the methods in the core one.
ColdBox Renderer Becomes a Singleton
The entire rendering mechanisms have changed in ColdBox 6 and we now support a singleton based approach to view rendering. It still allows for variable safety, but the way renderings in ColdBox 6 are done are orders of magnitude faster than pre ColdBox 6 days. If you are using applications like ContentBox or Preside CMS or applications with tons of renderView() calls, your applications will fly now!
LogBox Config Path Init
If you are using LogBox in standalone mode, you can now construct it by passing the path to your LogBox configuration file or no path at all and we will construct LogBox with our new default config file to stream logs to the console.
1 2 3 |
application.logbox = new LogBox();application.logbox = new LogBox( "config.MyLogBox" ); |
Release Notes
The full release notes per library can be found below.
ColdBox HMVC
Bugs
- [COLDBOX-48] - CacheBox creates multiple reap threads if the initial one take longer to complete than the reap frequency
- [COLDBOX-339] - Error in
AbstractFlashScope: key does't exists due to race conditions - [COLDBOX-822] -
InvalidEventis not working when set to a module event - [COLDBOX-829] - Stopgap for Lucee bug losing
sessionClusterapplication setting - [COLDBOX-850] - XML Converter Updated invoke() to correctly call method by name
New Features
- [COLDBOX-848] - Improve the bug reporting template for development based on whoops
- [COLDBOX-849] - Incorporate Response and RestHandler into core
- [COLDBOX-851] - All ColdBox apps get a
coldbox-tasksscheduler executor for internal ColdBox services and scheduled tasks - [COLDBOX-852] - Updated the default ColdBox config appender to be to console instead of the dummy one
- [COLDBOX-853] - ColdBox controller gets a reference to the AsyncManager and registers a new
AsyncManager@coldboxwirebox mapping - [COLDBOX-855] - Allow for the application to declare it's executors via the new
executorsconfiguration element - [COLDBOX-856] - Allow for a module to declare it's executors via the new
executorsconfiguration element - [COLDBOX-858] - Introduction of async/parallel programming via cbPromises
- [COLDBOX-859] - ability to do async scheduled tasks with new async cbpromises
Improvements
- [COLDBOX-830] - Update cachebox flash ram to standardize on unique key discovery
- [COLDBOX-833] - Improvements to threading for interceptors and logging to avoid dumb Adobe duplicates
- [COLDBOX-841] - Change announceInterception() and processState() to a single method name like: emit() or announce()
- [COLDBOX-846] - Use relocate and setNextEvent status codes in getStatusCode for testing integration
WireBox
Bugs
- [WIREBOX-90] - Fix constructor injection with virtual inheritance
New Features
- [WIREBOX-91] - Injector's get a reference to an asyncManager and a task scheduler whether they are in ColdBox or non-ColdBox mode
- [WIREBOX-92] - New
executorsdsl so you can easily inject executors ANYWHERE
Improvements
- [WIREBOX-88] - Improve WireBox error on Adobe CF
CacheBox
New Features
- [CACHEBOX-24] - CacheBox reaper : migrate to a scheduled task via cbPromises
- [CACHEBOX-60] - CacheFactory gets a reference to an asyncManager and a task scheduler whether they are in ColdBox or non-ColdBox mode
LogBox
Bugs
- [LOGBOX-38] -
Rotateproperty is defined but never used
New Features
- [LOGBOX-5] - Allow config path as string in LogBox init (standalone)
- [LOGBOX-11] - Allow standard appenders to be configured by name (instead of full path)
- [LOGBOX-36] - Added an
err()to abstract appenders for reporting to the error streams - [LOGBOX-42] - All appenders get a reference to the running LogBox instance
- [LOGBOX-44] - Rolling appender now uses the new async schedulers to stream data to files




Add Your Comment